Farrinstitute is reader-supported. We may receive commissions on purchases made through links on our site.
Low testosterone can result in fatigue, low libido, chronic disease, a lack of energy, and possibly cause you to lose muscle mass. Thankfully there are many ways to restore healthy testosterone levels, including exercise, dietary changes, and natural supplements.
However, not all exercises were created equal in their effect on testosterone production, as some workouts may cause your T levels to drop even further.
This article looks at the main types of exercise and how they affect your body’s T production.
Yes, exercise can not only help boost T levels and production but could result in lean muscle mass gain, losing weight, and in the case of physically active men and women, help them not gain weight [1, 2].
Exercise may also stimulate the release of growth hormone, which could promote weight loss and muscle growth [3].
Some forms of exercise can improve overall T levels, while others are better at enhancing your serum testosterone hormone values [4].
Below is an overview of some of the most popular forms of exercise chosen to boost T levels.
HIIT training is an excellent option for increasing testosterone in men. It is a full-body workout plan that focuses on alternating between short bursts of high-intensity exercise and even shorter rest periods.
A study comparing intensive-interval boost training and steady-state endurance exercise in men found the former elevated free testosterone more than the latter [5].
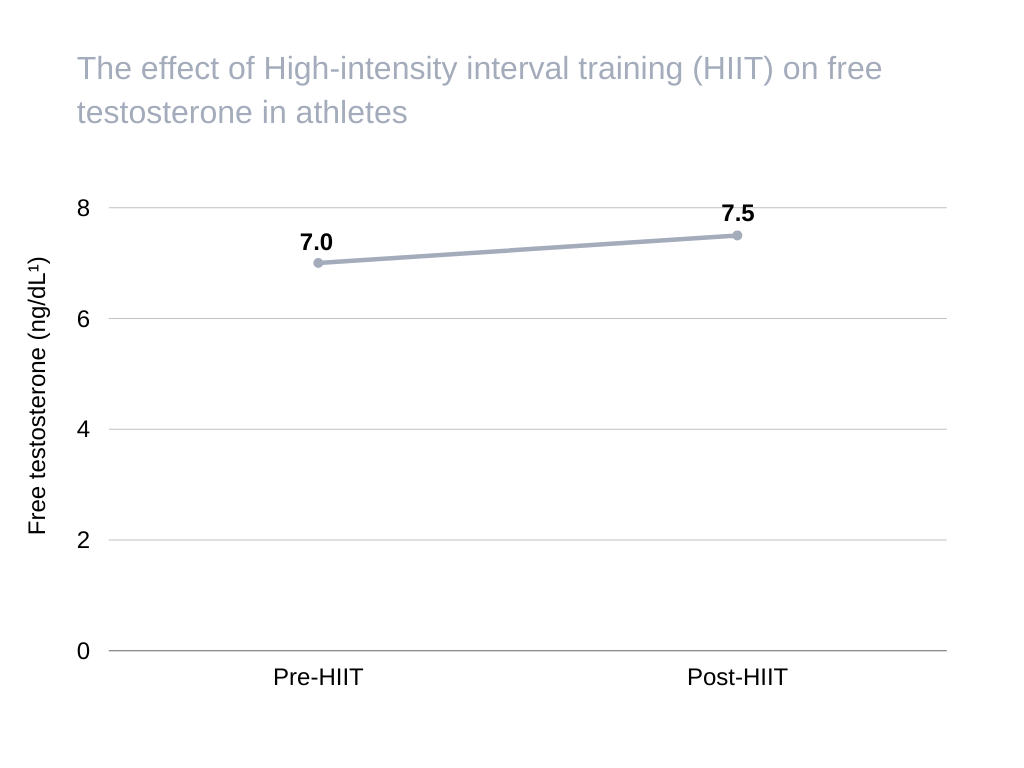
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5551442/
HIIT could also help boost total testosterone and SHBG concentrations in aging men [6].
Other benefits of HIIT include:
Unfortunately, HIIT for women does not boost T levels, with one study finding that the workout reduced T levels in women [7].
Both men and women can use resistance training to increase their levels of testosterone. Resistance exercise primarily consists of weightlifting, which is one of the best ways for men to boost their T levels.
Although women also respond well to resistance training to boost testosterone, the effect may not be as pronounced or long-lasting as males [8].
Yes, weight lifting and weight training can help elevate testosterone in men and women, although the increase may be more significant in males [9].
Strength training may also offer the following benefits [10]:
Below are some of the best workout routines you can follow to boost your T levels.
HIIT involves alternating between periods of intense exercise and rest. An example of a HIIT session is as follows:
HIIT training gets your heart pumping and can be cardio or weight-based. These timing and intensity intervals can be used for weights, squats, burpees, or even pull-ups.
Weightlifting requires targeting all your major muscle groups with various strength training exercises, including:
Lifting heavy weights is a great way to build muscle and burn fat, both of which could benefit your body’s long-term T production.
Resistance training is similar to weightlifting, although it may include a wider variety of exercises such as:
This training is an effective workout to boost testosterone in men and women while providing additional health benefits.
Crossfit is a hybrid of resistance training, HIIT, and cardio. It involves a full-body workout that activates all muscle groups and focuses on functional exercises like:
Striking sports like karate, boxing, taekwondo, and martial arts have also shown promise as forms of exercise that could boost T levels [11].
Some exercises that could simulate these effects include:
Some forms of exercise, like weightlifting, can raise testosterone by up to 21.6% in males and 16.7% in females [8]. However, these effects are typically acute, and resting testosterone levels are restored after around 30 minutes.
Exercise typically begins to raise testosterone as soon as it is started. Most T level increases are acute, and normal T levels will be restored soon after exercise stops.
Not all exercises work to boost T levels. Weight training and HIIT improve both T levels and muscle mass. Still, exercises that trigger the release of the stress hormone cortisol could effectively lower testosterone levels in men and women [12].
Endurance training like running long distances could result in long-term lowered T hormone levels in men and women [13]. Maximal aerobic exercise or cardio training can increase the concentration of the stress hormone cortisol in your body, which could cause your T hormone levels to drop.
Therefore, running and other endurance exercise forms are not recommended for trying to boost T levels.
Although cardio may help individuals of any gender lose weight and thereby increase their body’s T production, the exercise itself may reduce your overall T hormone levels due to excess cortisol production.
Yes, barbell squats can promote a significant short-term increase in the levels of testosterone in your body. These lower body exercises are also great for building muscle.
Low-intensity aerobic exercise like walking can boost your T levels, although this may be attributed more to overall weight loss than the exercise itself [14].
Like walking, jogging is a form of aerobic exercise that may prompt the increase in T levels due to the exercise itself and associated weight loss.
Pull-ups are part of strength training and therefore help raise T levels while also building muscle mass.
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about exercise and testosterone.
Working out can help women naturally boost their T, although not to the same extent as men. Fortunately, women are far less likely to experience symptoms of low testosterone compared to men.
Other than exercising, choosing a healthy diet, and getting quality sleep, you can naturally raise testosterone levels through dietary supplements.
Testogen, Test RX, and Testo Prime are three brands of T boosters that can help trigger T production in your body and combat effects like low libido.
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5870326/
Vitamin supplements, especially vitamin D, could also help improve your body’s T production, while vitamin D-rich foods and spending time in the sun could be equally effective.
For more information on what you can do to boost your testosterone, check out our articles on foods that kill testosterone, does soy increase estrogen in men, and foods that increase testosterone.
Weight training is the most effective exercise to naturally increase T levels in both men and women.
There is no evidence that masturbation causes low T hormone levels in men, although abstinence may elevate T levels slightly [15]
Exercise can be a very effective way of boosting T levels and combatting the effects of low T. However, other methods are also available, including dietary changes and using T boosters like Testogen, Test RX, and Testo Prime.
No matter the method you choose, raising your testosterone levels, especially if you are a male, could provide a range of long-lasting health benefits.